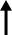|
| The National Pension Service's headquarters in Jeonju, North Jeolla Province / Yonhap |
By Kim Bo-eun
Korea's public pension fund is the world's third largest, with close to 1,000 trillion won ($763.3 billion) of assets under management, but there are concerns over the agency's ability to manage the fund.
The National Pension Service (NPS) faces the daunting task of reforming its pension system, as the fund is set to be depleted in the coming decades, with Korea's population aging rapidly. The pension fund had initially been estimated to become depleted in 2057, but more recent projections have indicated that it could end up depleted sooner.
The Federation of Korean Industries' research unit projects that the percentage of people aged 65 and older will rise from the current 17.3 percent to 37 percent in 2045, making South Korea the most aged country in the world. The federation forecasts that the pension fund will enter a deficit in 2039 and be depleted in 2055 under the current scheme.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare has initiated a process to calculate a more accurate estimate by March of next year, as part of a process to fix the pension system.
However, key leadership positions at the ministry remain vacant. The Yoon Suk-yeol administration has yet to appoint the minister of health and welfare despite Yoon having been inaugurated back in May. The ministry also oversees the pension agency. The NPS also does not have a CEO, after the former CEO stepped down in April.
The capacity of the NPS to manage assets has also come under fire. One problem is the difficulty in retaining talent, given the agency's relocation to Jeonju in 2017 from Seoul, as part of government efforts to decentralize and develop provincial areas.
Financial sector workers are eager to join the agency for their credentials, but many end up leaving within a few years, some because they do not wish to remain working in the provincial city 200 kilometers south of Seoul.
NPS has been increasing the number of fund managing positions but continues to face difficulty in securing personnel.
The situation is seen to have contributed to the agency's poor returns on investments. Data from the National Assembly Budget Office shows that the NPS' rate of returns on investments for 2021 is 10.86 percent, ranking below the figures of counterpart organizations in the U.S., Canada, Japan, Norway and the Netherlands, with comparable assets under management.
The Moon Jae-in administration had sought to develop the city of Jeonju into a financial district, centering on the NPS. Given opportunities to manage the agency's funds, the government had hoped to attract foreign financial firms to Jeonju, but there has been little interest from such entities.
"There is a reason why banks and financial institutions are concentrated in Seoul," Kim Sang-kyung, Korea International Finance Institute CEO and Korea Network of Women in Finance Chairperson, said. "Capability comes from competent people."
Kim Dae-jong, a professor of business at Sejong University, said the dispersal of state-run financial institutions has led to a loss in the competitiveness of the industry.
"In financial centers around the world, most key institutions are concentrated in one place, to facilitate operations," he said.
"The government should consider enabling the key investment personnel at the pension fund to be based in Seoul for such purposes," he said.
 Subscribe
Subscribe E-Paper
E-Paper