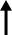An International Monetary Fund (IMF) team led by Mission Chief for Korea Rahul Anand, third from right, announces its findings on the Korean economy during a press conference at the Government Complex Seoul, Wednesday. The team wrapped up its 14-day visit here after an annual consultation with the government. Courtesy of Ministry of Economy and Finance
The International Monetary Fund's (IMF) mission team to Korea lowered the 2025 growth outlook for the country to 2 percent, Wednesday, from an earlier projection of 2.2 percent, citing heightened uncertainties and downside risks. This year's growth estimate was trimmed to 2.2 percent, down from 2.5 percent forecasted in October.
Underpinning the bleak outlook is a stagnant domestic spending and investment, despite strong chip exports. Uncertainty around the outlook remains high and risks are tilted to the downside in the years ahead, it added.
The assessment is in line with a recent wave of downward revisions for the Korean economy to between a range of low- to mid-2 percent. The Korea Development Institute and Korea Institute of Finance both slashed growth outlooks to 2.2 percent, from 2.5 percent. The finance ministry is expected to lower the previous forecast of 2.6 percent. Bank of Korea Governor Rhee Chang-yong said last month that the figure for this year will dip to 2.2 percent, down from the previous forecast of 2.4 percent in August.
"Strong semiconductor exports-oriented growth will be partially offset by a weak recovery of domestic demand," the team led by Mission Chief for Korea Rahul Anand said upon conclusion of 14-day annual consultation with financial authorities here. The mission met with officials of the Ministry of Economy and Finance, the Bank of Korea (BOK), the Financial Services Commission, the Financial Supervisory Service as well as state-run and private entities.
Read More
Tackling a declining labor force due to rapid population aging, enhancing capital allocation and bolstering productivity remain crucial to boost the growth potential, the team said.
"Advancing reforms would also help to enhance resilience in a changing environment characterized by geoeconomic fragmentation, technological changes, population aging and climate change.

Rahul Anand, second from right, the International Monetary Fund's (IMF) mission chief for Korea, is joined by his mission team members during a press conference at the Government Complex Seoul, Wednesday. Courtesy of Ministry of Economy and Finance
The IMF team said Korea's inflation is around the BOK's target of 2 percent, characterizing the gradual monetary policy normalization as "appropriate" given high uncertainty.
The authorities' envisaged fiscal consolidation and spending priorities in the 2025 budget proposal is appropriate, it added.
"Targeted policy efforts to address real estate-related financial risks are welcome, and the authorities should continue to monitor pockets of vulnerabilities and stand ready to act preemptively," it said. "If needed, additional prudential measures could be considered as monetary policy normalizes further."
Reinvigorating economic growth and strengthening resilience to the evolving global landscape are, it added, crucial priorities.
"A near-term mix of monetary normalization, exchange rate flexibility, gradual fiscal consolidation and targeted financial policies will help preserve macroeconomic stability and fortify the recovery."
 Subscribe
Subscribe E-Paper
E-Paper